RSA 算法 & 实现
算法介绍
RSA加密算法是一种非对称加密算法,所谓非对称,就是指该算法加密和解密使用不同的密钥,即使用加密密钥进行加密、解密密钥进行解密。在RSA算法中,加密密钥(即公开密钥)$PK$ 是公开信息,而解密密钥(即秘密密钥)$SK$ 是需要保密的。加密算法 $E$ 和解密算法$D$ 也都是公开的。虽然解密密钥SK是由公开密钥 $PK$ 决定的,由于无法计算出大数 $n$ 的欧拉函数 $\phi(N)$,所以不能根据 $PK$ 计算出 $SK$。
也就是说,对极大整数做因数分解的难度决定了 RSA 算法的可靠性。理论上,只要其钥匙的长度 $n$ 足够长,用RSA加密的信息实际上是不能被解破的。
RSA算法通常是先生成一对RSA密钥,其中之一是保密密钥,由用户保存;另一个为公开密钥,可对外公开。为提高保密强度,RSA密钥至少为500位长,一般推荐使用1024位。这就使加密的计算量很大。为减少计算量,在传送信息时,常采用传统加密方法与公开密钥加密方法相结合的方式,即信息采用改进的DES或IDEA密钥加密,然后使用RSA密钥加密对话密钥和信息摘要。对方收到信息后,用不同的密钥解密并可核对信息摘要。
公钥与私钥的生成
假设Alice想要通过一个不可靠的媒体接收Bob的一条私人信息。她可以用以下的方式来产生一个公钥和一个私钥:
- 随意选择两个大的素数 $p,q,p\ne q,N=pq$
- 根据欧拉函数,求得 ${\displaystyle r=\varphi (N)=\varphi (p)\times \varphi (q)=(p-1)(q-1)}$
- 选择一个小于 $r$ 的整数 $e$ ,使得 $e$ 与 $r$ 互质。并求得 $e$ 关于 $r$ 的模逆元,命名为 $d$(求 $d$ 令 $ed\equiv 1 \mod\ r$, 模逆元存在,当且仅当 ${\displaystyle e}$ 与 ${\displaystyle r}$ 互质)
- 将 ${\displaystyle p}$ 和 ${\displaystyle q}$ 的记录销毁。
${\displaystyle (N,e)}$ 是公钥,${\displaystyle (N,d)}$ 是私钥。Alice将她的公钥 $(N,e)$ 传给Bob,而将她的私钥 $(N,d)$ 藏起来。
加密消息
假设 Bob 想给 Alice 送一个消息 ${\displaystyle m}$ ,他知道 Alice 产生的 $N$ 和 $e$。他使用起先与 Alice 约好的格式将 $m$ 转换为一个小于 $N$ 的非负整数$n$ ,比如他可以将每一个字转换为这个字的 Unicode 码,然后将这些数字连在一起组成一个数字。假如他的信息非常长的话,他可以将这个信息分为几段,然后将每一段转换为 $n$。用下面这个公式他可以将$n$ 加密为 $c$ :
$c=n^e \mod N$
计算 $c$ 并不复杂。Bob算出 $c$ 后就可以将它传递给Alice。
解密消息
Alice 得到 Bob 的消息 $c$ 后就可以利用她的密钥 $d$ 来解码。她可以用以下这个公式来将 $c$ 转换为 $n$ :
$n=c^d\mod N$
得到 $n$ 后,她可以将原来的信息 ${\displaystyle m}$ 重新复原。
解码的原理是
$c^d\equiv n^{e\cdot d}\mod N$
已知 $ed\equiv 1\mod r$,即 $ed=1+h\phi(N)$。那么有
$n^{ed}=n^{1+h\phi(N)}=n\cdot n^{h\phi(N)}=n\cdot (n^{\phi(N)})^h$
若 $n$ 与 $N$ 互素,则由欧拉定理得
$n^{ed}\equiv n\cdot (n^{\phi(N)})^h \equiv n(1)^h\equiv n\mod N$
若 $n$ 与 $N$ 不互素,则不失一般性考虑 $n=ph$,以及 $ed-1=k(q-1)$,得:
$n^{ed}=(ph)^{ed}\equiv 0\equiv ph\equiv n\mod p$
$n^{ed}= n^{ed-1}n=n^{k(q-1)}n=(n^{q-1})^kn\equiv1^kn\equiv n\mod p$
故 $n^{ed}\equiv n\mod N$ 得证
实现细节
密钥生成
首先要使用概率算法来验证随机产生的大的整数是否质数,这样的算法比较快而且可以消除掉大多数非质数。假如有一个数通过了这个测试的话,那么要使用一个精确的测试来保证它的确是一个质数。
除此之外这样找到的 $p$ 和 $q$ 还要满足一定的要求,首先它们不能太靠近,此外 $p-1$ 或 $q-1$ 得因子不能太小,否则的话 $N$ 也可以被很快分解。
此外寻找质数的算法不能给攻击者任何信息,这些质数是怎样找到的,尤其产生随机数的软件必须非常好。要求是随机和不可预测。这两个要求并不相同。一个随机过程可能可以产生一个不相关的数的系列,但假如有人能够预测出(或部分地预测出)这个系列的话,那么它就已经不可靠了。比如有一些非常好的随机数算法,但它们都已经被发表,因此它们不能被使用,因为假如一个攻击者可以猜出 $p$ 和 $q$ 一半的位的话,那么他们就已经可以轻而易举地推算出另一半。
此外密钥 $d$ 必须足够大,1990年有人证明假如 $p$ 大于 $q$ 而小于 $2q$ 这是一个很常见的情况)而 $d<\frac{1}{3}\times N^{\frac{1}{4}}$,那么从 $N$ 和 $e$ 可以很有效地推算出 $d$。此外 $e=2$ 永远不应该被使用。
64bit RSA 算法实现
密钥生成
生成 e, d, N。根据标准 e 取 65537,如果 e 和 $\phi(N)$ 不互质,那么就重新选取 p, q。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#define DEFAULT_E 65537
typedef unsigned long u64;
void key_generation(s64 *N, s64 *e, s64*d) {
s64 p, q, phi_N;
*e = DEFAULT_E;
do {
set_primes(&p, &q, N, &phi_N);
} while (!is_e_valid(*e, phi_N));
*d = find_d(*e, phi_N);
}
set_primes: 生成 p,q,N。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
void set_primes(s64 *p, s64 *q, s64 *N, s64 *phi_N) {
get_prime_32bit(p);
do {
get_prime_32bit(q);
} while (*p == *q);
*N = (*p) * (*q);
*phi_N = (*p - 1) * (*q - 1);
}
is_e_valid: 检验 e 是否合法,即是否与 $\phi(N)$ 互素。
1
2
3
int is_e_valid(s64 e, s64 phi_N) {
return gcd_s64(e, phi_N) == 1;
}
gcd_s64: 求最大公约数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
s64 gcd_s64(s64 a, s64 b) {
int tmp;
while (b) {
tmp = b;
b = a % b;
a = tmp;
}
return a;
}
find_d: 计算 e 的乘法逆元 d。
1
2
3
4
5
6
s64 find_d(s64 e, s64 phi_N) {
s64 x, y;
exgcd(e, phi_N, &x, &y);
x = (x % phi_N + phi_N) % phi_N;
return x;
}
exgcd:扩展欧几里得算法求乘法逆元
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
s64 exgcd(s64 a, s64 b, s64 *x, s64 *y)
{
s64 xi_1, yi_1, xi_2, yi_2;
xi_2 = 1, yi_2 = 0;
xi_1 = 0, yi_1 = 1;
*x = 0, *y = 1;
s64 r = a % b;
s64 q = a / b;
while (r) {
*x = xi_2 - q * xi_1;
*y = yi_2 - q * yi_1;
xi_2 = xi_1;
yi_2 = yi_1;
xi_1 = *x, yi_1 = *y;
a = b;
b = r;
r = a % b;
q = a / b;
}
return b;
}
加密
1
2
3
4
5
void cipher_decipher(s64 *in, int len, s64 *out, s64 e, s64 N) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
out[i] = cipher_s64(in[i], e, N);
}
}
利用快速幂进行加密
1
2
3
s64 cipher_s64(s64 in, s64 e, s64 N) {
return qpow(in, e, N);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
s64 qpow(s64 a, s64 b, s64 p) {
s64 ans = 1;
a = (a % p + p) % p;
for (; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) ans = (a * ans) % p;
a = (a * a) % p;
}
return ans;
}
解密
与加密一致
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
void test() {
s64 e, d, N;
s64 text[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
s64 cipher_text[sizeof(text) / sizeof(s64)];
s64 decipher_text[sizeof(text) / sizeof(s64)];
int len = sizeof(text) / sizeof(s64);
printf("key generating...\n");
key_generation(&N, &e, &d);
printf("e : %lu\nd : %lu\nN : %lu\n", e, d, N);
printf("encrypting...\n");
printf("text : ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) printf(" %x" + !i, text[i]);
printf("\n");
cipher_decipher(text, len, cipher_text, e, N);
printf("cipher text : ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) printf(" %x" + !i, cipher_text[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("decrypting...\n");
cipher_decipher(cipher_text, len, decipher_text, d, N);
printf("decipher text : ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) printf(" %x" + !i, decipher_text[i]);
printf("\n");
if (memcmp(text, decipher_text, len * sizeof(s64))) {
printf("failed, e : %u, d : %u, N : %u\n", e, d, N);
} else {
printf("success\n");
}
}
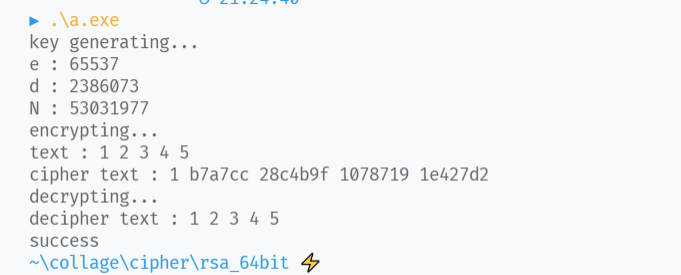
运行结果:
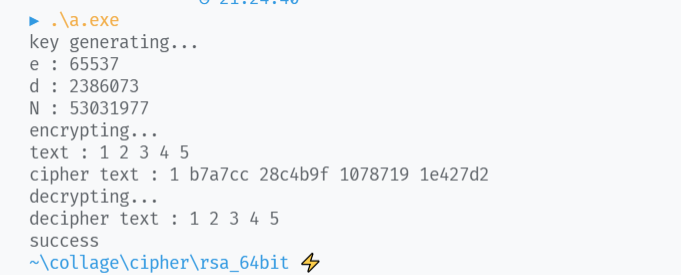
1024bit RSA 算法实现
实现需要注意的问题
Open MPI
密钥长度为1024bit,超过了最大数据类型long long的64位,需要高精度运算,下面介绍一个高性能并行计算库 Open MPI,详细可以参考资料3。
The Open MPI Project is an open source Message Passing Interface implementation that is developed and maintained by a consortium of academic, research, and industry partners. Open MPI is therefore able to combine the expertise, technologies, and resources from all across the High Performance Computing community in order to build the best MPI library available. Open MPI offers advantages for system and software vendors, application developers and computer science researchers.
这个库在网络上的资料目前还比较少,linux 中 RSA 实现使用的是 Open MPI。
GNU MP
下面介绍另外一个高精度计算库,GNU MP。
GMP is a free library for arbitrary precision arithmetic, operating on signed integers, rational numbers, and floating-point numbers. There is no practical limit to the precision except the ones implied by the available memory in the machine GMP runs on. GMP has a rich set of functions, and the functions have a regular interface.
详细资料参考资料4。
密钥生成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#define PRIME_LENGTH 512
unsigned long GMP_SEED = 233;
typedef struct
{
mpz_t e;
mpz_t N;
mpz_t d;
} rsa_key;
void key_generation(rsa_key *key) {
gmp_randstate_t state;
mpz_set_ui(key->e, 65537);
mpz_t p, q;
mpz_inits(p, q, NULL);
init_random_state(state);
get_prime(p, state);
init_random_state(state);
get_prime(q, state);
mpz_mul(key->N, p, q);
mpz_t p_minus1, q_minus1, phi_N;
mpz_inits(p_minus1, q_minus1, phi_N, NULL);
mpz_sub_ui(p_minus1, p, 1);
mpz_sub_ui(q_minus1, q, 1);
mpz_mul(phi_N, p_minus1, q_minus1);
mpz_clears(p, q, p_minus1, q_minus1, NULL);
mpz_invert(key->d, key->e, phi_N);
}
质数生成算法,采用 Donald E.Knuth《计算机程序设计艺术 第2卷 半数值算法》 中的素性测试算法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void get_prime(mpz_t p, gmp_randstate_t state) {
mpz_rrandomb(p, state, PRIME_LENGTH);
while (!(mpz_millerrabin(p, PRIME_LENGTH))) {
gmp_randclear(state);
GMP_SEED++;
init_random_state(state);
mpz_rrandomb(p, state, PRIME_LENGTH);
}
gmp_randclear(state);
GMP_SEED++;
}
void init_random_state(gmp_randstate_t state) {
gmp_randinit_mt(state);
gmp_randseed_ui(state, GMP_SEED);
}
逆元生成则直接调用 GNU MP 中 mpz_invert 函数计算。
加密
decode 将一个结构解码为 mpz 类型。然后使用 encrypt 进行加密。
1
2
3
4
5
6
void rsa_encrypt(mpz_t cipher_text, mpz_t plain_text, rsa_key *key) {
mpz_powm(cipher_text, plain_text, key->e, key->N);
}
void rsa_decode(mpz_t decode, unsigned char decode_arr[]) {
mpz_import(decode, 128, 1, sizeof(decode_arr[0]), 0, 0, decode_arr);
}
解密
与加密类似。
1
2
3
4
5
6
void rsa_decrypt(mpz_t decrypt_text, mpz_t cipher_text, rsa_key *key) {
mpz_powm(decrypt_text, cipher_text, key->d, key->N);
}
void rsa_encode(mpz_t encode, unsigned char encode_arr[]) {
mpz_export(encode_arr, NULL, 1, sizeof(encode_arr[0]), 0, 0, encode);
}
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
void test() {
rsa_key key;
mpz_t plain_text, cipher_text, decrypt_text;
mpz_inits(key.e, key.N, key.d, NULL);
mpz_inits(plain_text, cipher_text, decrypt_text, NULL);
unsigned char plain_text_arr[128] = "hello world!";
unsigned char decrypt_text_arr[128];
gmp_printf("generating key...\n");
key_generation(&key);
gmp_printf("e : %Zd\nd : %Zd\nN : %Zd\n", key.e, key.d, key.N);
gmp_printf("encrypting...\n");
rsa_decode(plain_text, plain_text_arr);
gmp_printf("plain text : %s\n", plain_text_arr);
gmp_printf("plain text val : %Zd\n", plain_text);
rsa_encrypt(cipher_text, plain_text, &key);
gmp_printf("decrypting...\n");
rsa_decrypt(decrypt_text, cipher_text, &key);
rsa_encode(decrypt_text, decrypt_text_arr);
gmp_printf("decrypt text : %s\n", decrypt_text_arr);
gmp_printf("decrypt text val : %Zd\n", decrypt_text);
}
测试结果: